Knowing when to take profits on stocks is one of the most critical yet challenging aspects of trading.
The dilemma of whether to secure gains or let them ride can make the difference between consistent profitability and missed opportunities. This is where having a clear set of profit taking strategies becomes essential. These strategies provide a disciplined framework for deciding how to take profit from a winning position, helping you lock in gains and manage risk effectively.
In this guide, we will explore the most effective profit-taking strategies and provide a practical profit taking strategy example for various market conditions, empowering you to exit trades confidently and maximize your returns.
Best Profit Taking Strategies
Deciding when to take a profit based on fundamentals or macroeconomic situations is one thing; deciding how to take profits in order to gain maximally is quite another.
Do you set random take-profit orders after certain percentage gains, or should your profit-taking plan include taking gains at certain regions of resistance — such as pivot points and Fibonacci levels? Smart traders and investors consider all of the above before execution.
Let us dive into some of the popular profit-taking strategies:
Take Profit based on Trends: Trend Following Exits
Moving averages are important to all trading strategies. Since the creation of indicators, the moving average has been one of the most commonly utilized ways of entering and exiting the market.
The advantage of using moving averages for take profits is their simplicity. And, if you prefer exits that don’t take up a lot of your time, the moving average exit is among the best.
Taking a profit using moving averages work best in trending markets.
For example, consider the simple moving average crossover exits at 5 and 20 periods.
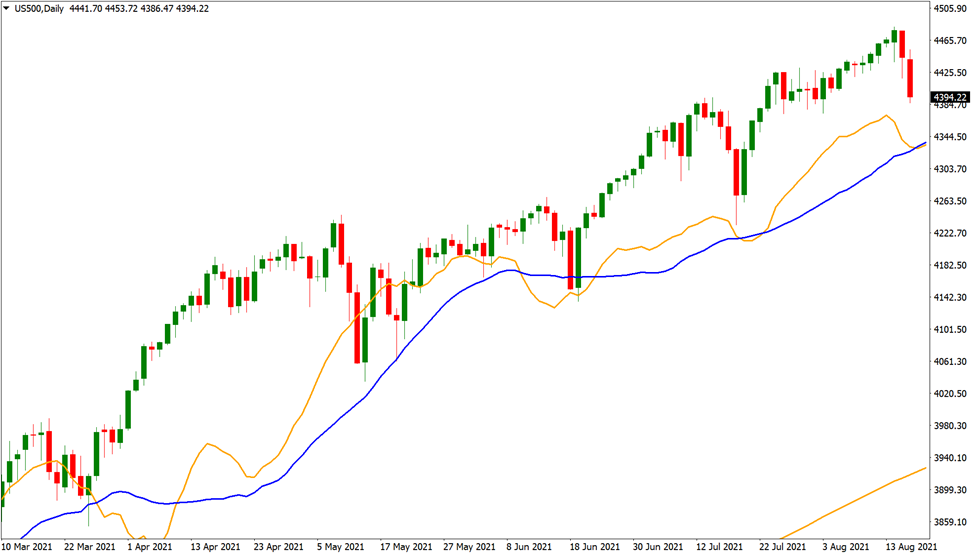
As shown in the figure above, the US500 experienced a strong bull run in H1 2021.
The 5 and 20-period moving average exits are as straightforward as they get.
You take a profit when the 5-period (blue line) crosses below the 20-period (maroon line).
As the chart above shows, it would have generated an acceptable run on the US500, giving you a great opportunity to profit.
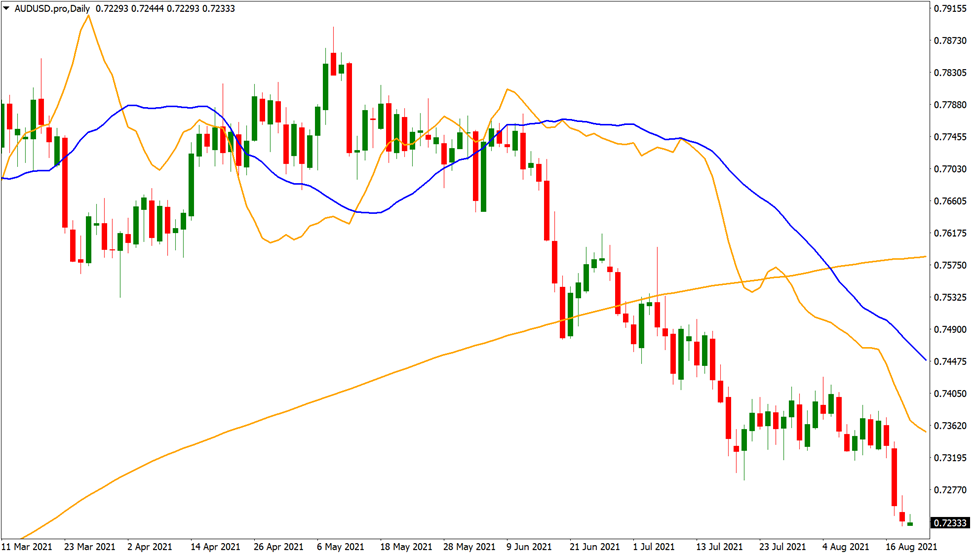
The chart above depicts a consolidation period on AUD/USD when this type of exit becomes ‘choppy’. This implies that you are receiving exit indications more frequently because there is no trend in place.
Furthermore, if you use the same indication to enter the trade, you will be chopped in and out, causing a sequence of small losses and breakeven transactions.
Taking Profits with Chandelier Exit: ATR Based Trailing Stops
The Chandelier Exit is a volatility-based trailing stop strategy that uses the Average True Range (ATR) to dynamically adjust its position. By anchoring to a recent high (in an uptrend) or low (in a downtrend), it “hangs” the stop like a chandelier from the ceiling of the trade.
This approach automatically adapts to market conditions:
- In high-volatility periods, the ATR value increases, placing the stop-loss further away to avoid being exited by normal market noise.
- In low-volatility periods, the ATR decreases, tightening the stop and helping to protect a larger portion of unrealized gains.
Common parameters for a long trade are:
- Trend-Following:Exit = (22-day High) – (3 x ATR(22))
- Short-Term:Exit = (22-day High) – (2 x ATR(22))
This method systematically locks in profits while giving a trade sufficient room to develop, making it a cornerstone of many disciplined trading systems.
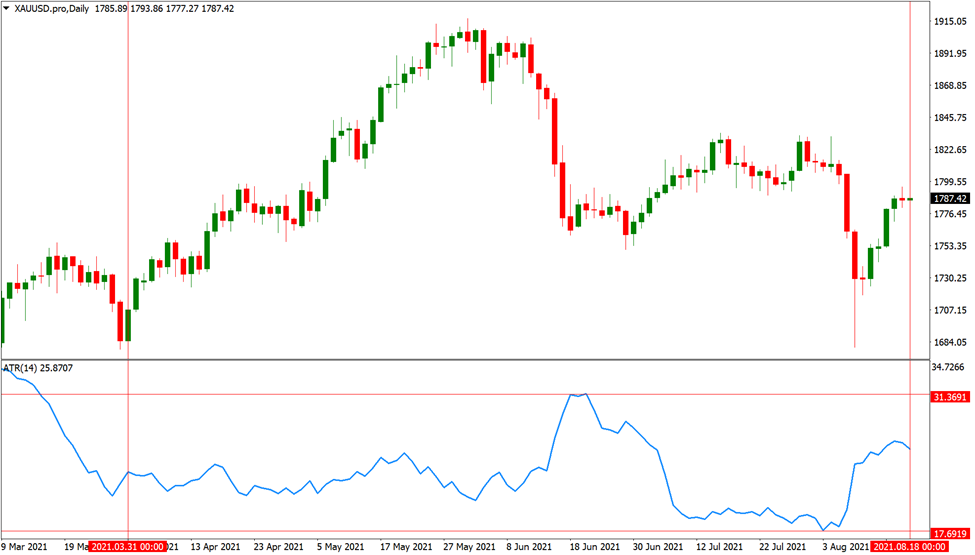
The accompanying gold data shows that the ATR fluctuated from 17.70 to 31.37 between April 2021 and mid-August 2021. This indicates that during this period, the greatest volatility of gold was about $31 per day.
The primary advantage of this type of profit taking strategy is that it lowers your odds of receiving an early exit by letting the market volatility determine when to exit.
Your chances of being whipsawed out of your trade during periods of extreme volatility will significantly increase if you set your exit at, let’s say, $10.
The nice thing about this profit-taking strategy is that it automatically calculates your ATR each day, so you can utilize that data to modify your exits.
Use Support and Resistance for Take a Profit
Another take-profit strategy is setting profit targets based on support and resistance lines. If you observe a range-bound stock, Forex pair, or crypto, you may want to profit from the movement by purchasing weakness at the lower end of the range and selling strength at the upper end.
The NZD/CAD price chart above illustrates a range-bound phase where the currency pair consolidated inside a range of 300 pips. You may schedule a profit-taking exit before the key 0.89 resistance level if you bought weakness on support.
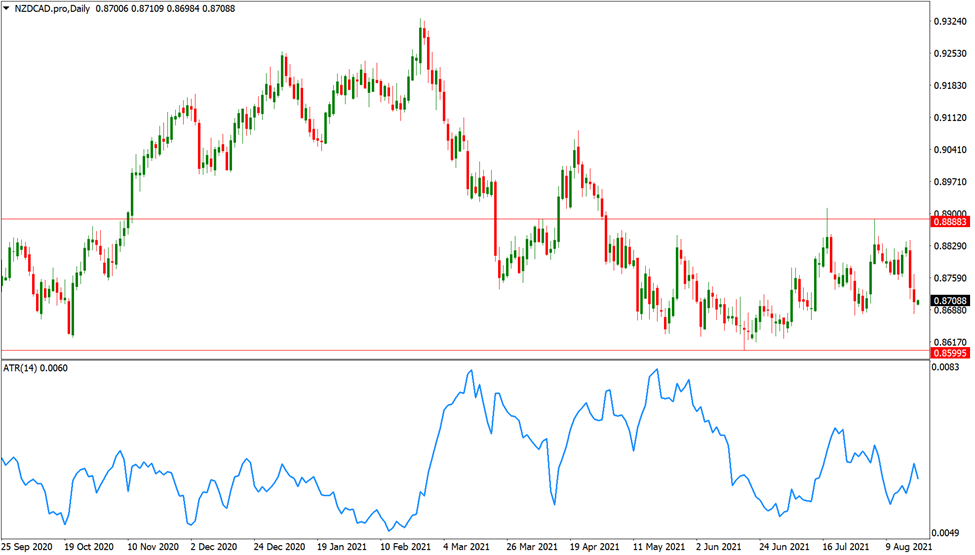
Consider the scenario where you were receiving entry signals before the 0.86 support level, and you might have positioned your take-profit level immediately before 0.89.
Profit-Taking strategy Based on Fundamental Data
Decisions about stock positions in fundamental analysis are significantly influenced by external information.
It could be wise to think about taking profits if, for example, a rival company like Morgan Stanley or Bank of America produces a poor report or if the entire financial industry underperforms in comparison to other sectors.
Some other fundamental news that you might consider when trading the financial markets include:
- Inflation data
- GDP figures
- Central Bank rate decisions
- NFP results and all unemployment data
- FOMC and ECB meeting
But in the present case, GS Bank’s basic foundation seems solid. Remaining cautious while taking profits is advised since there are no unfavorable reports from rivals, and the banking sector is generally strong.
Robust fundamentals offer a strong base for prospective future growth, strengthening the case for holding the position and profiting from the stock’s long-term strength.
Take a Profit when Divergence Signals
One of the best signs for trading any kind of instrument is divergence. Both bearish and bullish divergences are utilized.
A bullish divergence occurs when the price hits a lower low, but the technical indicator – ideally an oscillator like the stochastic or RSI- makes a higher low.
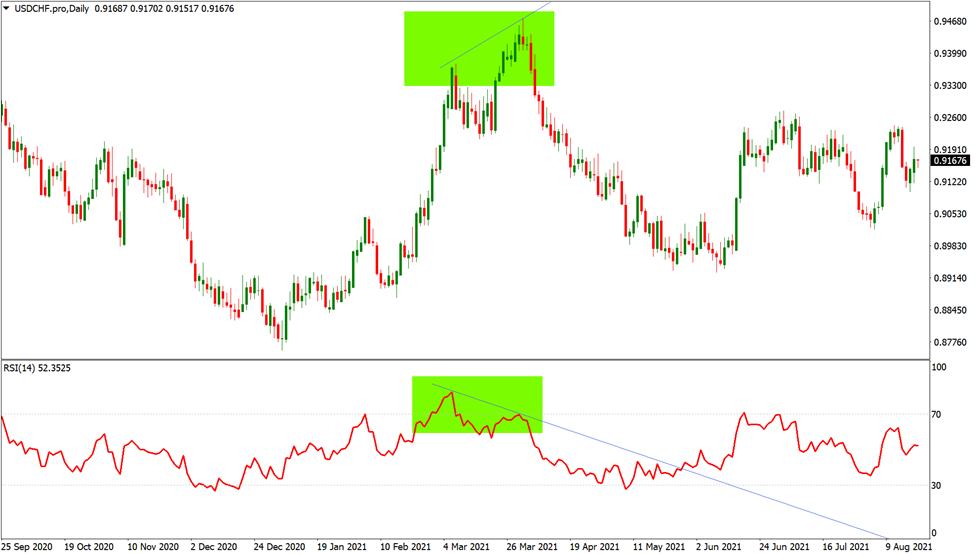
Suppose you were long USD/CHF at the low of December 2020. However, by the middle of March, the daily chart displayed a bearish RSI divergence.
In this situation, you could decide to close the trade depending on the bearish divergence before the correction gains significant momentum.
Time-Based Exit Strategies
Successful trades typically begin to work in your favor right away. On the other hand, certain transactions will stand still for a long time.
A trader who trades intraday may choose to exit the market in just ten minutes, while an end-of-day trader may wait five days for sideways movement before closing. You must adjust your time-based exit depending on how long you plan to trade.
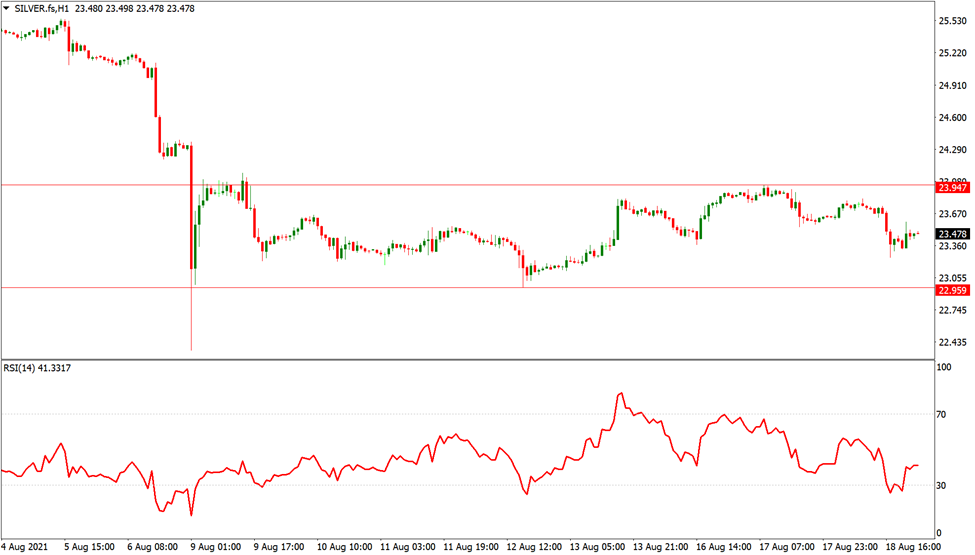
A short-term trader would have found it difficult to endure the consolidation phase depicted in the silver hourly chart above.
How do You Develop an Profit Taking Strategy?
To properly identify an acceptable profit taking strategy, first evaluate your overall investment strategy and the type of trader you are. Opening and closing transactions based on gut feelings is challenging, and many traders (particularly beginners) would gain from having a laid-out approach and an already-prepared trading plan.
The plan should specify how you will choose your entry point as well as your stop losses and take profit levels. Adhering to them is critical; otherwise, you may end up allowing your losing positions to run wild in the expectation that the market price will eventually shift in your favor while slicing your winning positions short since you believe you must bank that gain before the price moves against you.
Factors that Determine Profit-Taking
- Observe Bearish Chart Patterns: If you see a bearish trend in the market, it’s the correct time for profit-taking. Keep a watch out for these indicators.
- Stagnant Prices: If prices remain static for an extended period and do not move upward, it is time to consider an exit technique.
- Recognize Divergence Patterns: This occurs when technical indicators move against price fluctuations. This pattern happens when the price falls but is not represented in the indicator, and it could signal an upward trend.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Technical analysis using Fibonacci retracement levels can identify market trends by comparing high and low points. Fibonacci ratios show the extent to which the price has retraced.
- Uncertain Macroeconomic Conditions: Situations like pandemics, inflation, employment levels, price changes, considerable financial growth, war, or political events in a country also affect trading decisions.
- Fundamental Analysis: Analyze the market to understand what other traders are doing. This investigation could include what they’re investing in and how much.
- Risk Tolerance: Each trader has a unique risk tolerance and investing style. Some traders have a low-risk tolerance and prefer to play long-term. Others prefer fast, steady profits and are inclined to play along with the market’s highs and lows.
Tips for Taking Profit Effectively
- Monitor the Stock Index: Track pertinent stock indices to stay up to date on general market shifts. Understanding the general market trend offers useful context for determining when to take profits from particular security.
- Keep up with the News: Pay careful attention to happenings and news in the business world. News can have an impact on stock prices, so keeping up with pertinent developments can help you decide when to take profits or modify your positions.
- Recognize when Everyone is Greedy: “Be fearful when others are greedy, and greedy when others are fearful,” as Warren Buffett once said. When extreme greed rules the market, take note of the sentiment and proceed with caution since this could be a sign of an overheated market.
- Segment your Profits: Selling some portion of your stake could help you take a more progressive approach to taking profits. This approach strikes a balance between earning profits and sticking with your investment by allowing you to secure certain profits while keeping you exposed to possible further upside.
Understanding Take-Profit Orders
Take profits are orders set by traders to sell an asset automatically when it reaches a particular price level, locking returns and reducing prospective losses.
A take-profit order is a crucial trading tool. It is essentially a form of limit order that serves only one purpose: to designate the exact price at which you want to close an open position to secure a gain. However, unless the security’s price reaches the specified maximum, the take-profit order will remain pending and unexecuted.
These orders are typically used together with stop-loss orders, forming a dynamic duo for successful risk management. When the security’s price moves to the take-profit point, the take-profit order is triggered, resulting in the position being closed with a profit. In contrast, if the security’s price falls below the stop-loss level, the stop-loss order is executed, resulting in a predetermined loss. This precise interplay between take-profit and stop-loss levels assists traders in determining the risk-reward ratio for every trade.
The Significance of Take-Profit Orders
It goes without saying that a trader’s take-profit strategy is just as crucial as their stop-loss placement. The reward-to-risk ratio takes into account both variables.
Take profits significantly and directly impact the reward side of the risk-to-reward ratio. This ratio evaluates and calculates the trade’s prospective profit and loss.
Besides, securing the gain is an important aspect of trading success as it is the only time a trader actually makes a profit. Any paper or floating profit from an open trade has no value until it is closed and booked.
The usefulness of take-profit orders stems from their power to automate trading choices. Traders can predetermine their profit targets, minimizing the need for manual intervention and the human tendency to second-guess judgments. However, there is a catch: take-profit orders function at the best attainable price, irrespective of the security’s performance. As a result, a stock may venture on a breakout, but the take-profit order could be triggered at the very beginning, potentially resulting in missed opportunities.
Moreover, take-profit orders are especially preferred for short-term trading that seeks to manage risk adequately. Short-term traders intend to exit positions as soon as their predefined profit target is met, avoiding exposure to possible market downturns. Long-term investors, on the other hand, often avoid such orders since they have the ability to reduce potential profits over time.
These orders are frequently placed based on a range of technical and analytical variables, such as support and resistance levels, chart pattern analysis, or the use of money management strategies like the Kelly Criterion. Additionally, many trading system developers use take-profit orders to execute automated trades because they provide a well-defined risk management structure.
Conclusion
As it is evident from the examples above, as well as from hundreds of stock success stories, the right profit-taking strategies can help you earn with stocks time and again. The idea is to pay attention to risk and keep losses small to continue trading till you get more winning trades. Experienced investors and traders know when it is time to take a profit. They frequently employ a variety of techniques to earn profits, but the foundation of any technique should always be a thorough comprehension of the market’s fundamentals and the attitudes of the investors that influence price movements.
FAQ
How Can I Take Profit Without Exiting My Entire Trade?
This is one of the most important questions for moving from a beginner to an intermediate trader. The core idea is to exit your position in portions, which allows you to bank profits on part of your trade while letting the remainder run to capture potential further gains.
This approach balances the psychological need for security with the strategic goal of maximizing successful trends.
- Locks in Gains: It turns “paper profits” into real money, securing your reward for the risk you took.
- Reduces Psychology Pressure: Once a portion is profitably closed, the trade is often “in the money,” reducing the stress of a winner turning into a loser. This makes it easier to manage the remaining position.
- Lets Profits Run: By taking some profit off the table, you can trail your stop-loss on the remaining position more aggressively, allowing you to participate in extended trends without fear.
- Creates a Positive Feedback Loop: Consistently banking partial profits builds confidence and reinforces disciplined trading habits.
Common Strategies for Taking Partial Profits:
- 1. Scaling Out (The Most Popular Method)
This involves exiting a predetermined percentage of your position at specific price levels.
If you buy 3 lots of a currency pair, you might sell 1 lot when price hits a 1:1 Risk/Reward (R/R) ratio, another lot at 1.5:1 R/R, and let the final lot run with a trailing stop until the trend reverses. - 2. Using Technical Levels (Support & Resistance).
You take profit as the price approaches or touches key technical areas.
If a trade is moving up, you take partial profits as it hits a previous swing high, a significant Fibonacci extension level (e.g., 127.2% or 161.8%), or a major resistance zone. - 3. The “Profit Stop” or “Stop to Breakeven + Partial Close”
This is a powerful psychological and risk management technique.
Once a trade moves in your favor by a certain amount (e.g., 1.5x your initial risk), you do two things simultaneously:- a) Close a portion of your trade (e.g., 30-50%).
- b) Move your stop-loss on the remaining position to your entry point (breakeven).
- Trailing Stop with a Partial Close.
You combine a trailing stop with an initial partial profit target.
You set a fixed profit target for, say, 50% of your position. Once that target is hit, you remove the initial stop-loss on the remaining 50% and switch to a trailing stop (e.g., based on ATR or a moving average) to capture the trend.
When Should You Take Profits on Stocks?
There’s no single “right” time, but successful traders use predefined strategies, not emotion. Here are the most common approaches:
- At Technical Levels: Take profits when the stock hits key resistance, a major Fibonacci extension level, or when the momentum (e.g., RSI) becomes overbought. This is based on the chart’s structure.
- By Scaling Out: Don’t exit your entire position at once. Sell a portion (e.g., ½ or ⅓) at your first price target. This locks in gains and lets you participate in further upside with the remaining shares, often with a trailing stop.
- When Your Thesis Changes: If the fundamental reason you bought the stock (e.g., strong earnings growth, a new product) is no longer valid, it’s time to take profits and move on.
- Using a Risk/Reward Ratio: Before you buy, decide your exit point. For example, if you risk $1 per share, aim to take profits at a $2 or $3 gain. This ensures your winners are larger than your losers.
The Golden Rule: Your profit-taking strategy should be part of your initial trade plan. This removes emotion and leads to more disciplined, consistent results.
What is a Good Take-Profit Percentage for a Trade?
There is no universal “good” percentage, as it depends entirely on your strategy and the market environment. However, the core principle is to base your profit target on the trade’s context, not a fixed number.
Here’s how to determine it:
- Use the Risk/Reward Ratio: This is the most critical concept. Your profit target should be a multiple of your initial risk.
A common benchmark is a 1:2 or 1:3 ratio. If you risk 2% of your capital, aim for a 4-6% profit. This means you can be profitable even if you win only 40-50% of your trades. - Base it on Technical Analysis: Your profit target should be set at a logical price level, not a random percentage.
Look for the next level of significant resistance (for a long trade) or support (for a short trade).
Use tools like Fibonacci extensions or measure the height of a chart pattern (like a triangle or channel) to project a realistic target. - Consider Scaling Out: Instead of one target, use multiple. For example:
Take 50% of your position off at a 1:1 risk/reward.
Take another 25% off at 1:2.
Let the final 25% run with a trailing stop to capture a larger trend.
In short: A “good” take-profit percentage is one that is defined by your trading plan and provides a risk/reward ratio of at least 1:1.5 or higher, based on the market’s own structure.
Backtest Library
We all have that one indicator we keep coming back to, but how do we know if it’s truly effective or just a comforting habit?
At QuantStrategy, we believe in validation through data.
That’s why we’ve built a library of backtests on foundational tools like the industry standard indicators and exit strategies.
Curious about the specific win rate, maximum drawdown, and overall performance of strategies on the 6000+ stocks?
We’ve done the heavy lifting.
Click here to explore the full backtest report and turn your market curiosity into a strategic edge.